- Home
- Plastic at Home
- Plastic Recycling Codes
- Energy Recovery
Energy Recovery: Turning Waste Into Usable Energy
In our daily lives, we all contribute to a waste stream that demands thoughtful management. While recycling remains a cornerstone of environmental responsibility, another method, often overshadowed, holds immense value as a complementary approach: energy recovery.
Let's explore how this innovative process is shaping a more sustainable future.

What is Energy Recovery?
Energy recovery refers to the process of extracting usable energy from waste materials. Unlike traditional recycling, which repurposes waste into new products, energy recovery focuses on converting the waste's inherent energy into different forms like heat, electricity, or fuel, helping to reduce the volume of waste that ends up in landfills.. This process can occur through various methods, including incineration, anaerobic digestion, and gasification.
Key Methods of Energy Recovery
The methods are diverse and vary in their technological approaches and the types of waste they can process. Here are the three primary methods: incineration, anaerobic digestion, and gasification and pyrolysis.
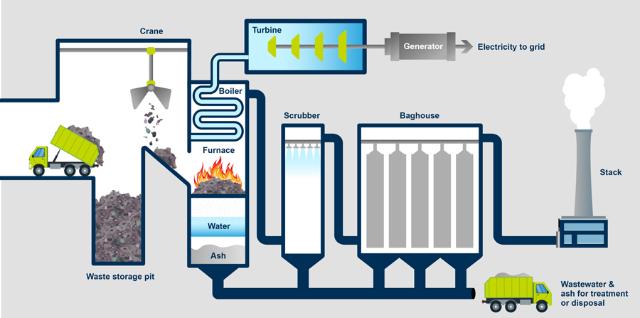
1. Incineration
Incineration is the most common method of extracting energy from waste. Waste materials are burned at high temperatures, producing heat that can be directly used for district heating systems or converted into steam to drive turbines for electricity production. This makes incineration a dual-purpose solution, managing waste and generating energy.
2. Anaerobic Digestion
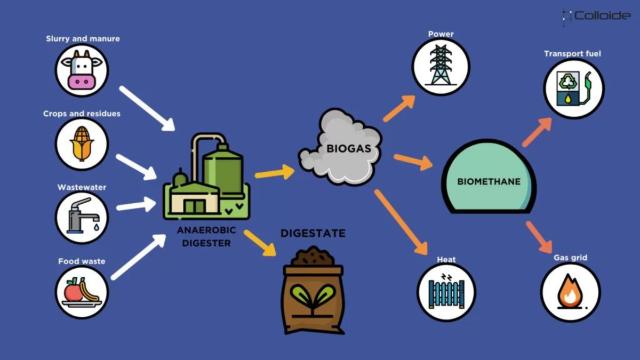
Anaerobic digestion involves breaking down organic waste (such as food scraps and agricultural waste) in the absence of oxygen. Organic waste is placed in a sealed, oxygen-free tank called a digester. Over time, microorganisms break down the waste, producing biogas and digestate (a nutrient-rich residue).
The biogas generated is a mixture of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), with small amounts of other gases. Methane, being the main component, is a valuable energy source. It can be used to generate electricity and heat, or it can be purified and upgraded to biomethane, which is suitable for injection into the natural gas grid or use as vehicle fuel. On the other hand, the digestate produced can be used as a fertilizer or soil conditioner, recycling nutrients back into the soil and supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
3. Gasification and Pyrolysis
Gasification and pyrolysis are advanced thermal processes that convert waste materials into syngas (synthetic gas) under controlled conditions, typically with limited or no oxygen. These processes are highly versatile and can handle various types of waste, including biomass, plastics, and municipal solid waste.
Both gasification and pyrolysis are cleaner compared to traditional combustion. They produce fewer emissions and allow for more controlled and efficient energy recovery.
Benefits of Energy Recovery
1. Waste Volume Reduction
The above mentioned energy recovery methods significantly reduce the volume of waste that needs to be landfilled. Incineration, for example, can reduce the volume of waste by up to 90%. This reduction is particularly beneficial in densely populated areas where landfill space is limited. By minimizing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills, energy recovery helps mitigate the environmental impacts associated with waste disposal, such as leachate production and land degradation.
2. Energy Production
Converting waste into energy provides a valuable source of heat, electricity, and fuel. This process reduces reliance on fossil fuels and supports the integration of renewable energy sources into the energy grid. For instance, waste-to-energy plants can generate electricity and district heating, contributing to energy security and reducing the environmental footprint of energy production. Additionally, the energy produced from waste can be used locally, providing a reliable and continuous energy supply.
3. Resource Conservation
Utilizing waste for energy helps conserve natural resources by reducing the need for raw materials and fossil fuels. This contributes to a more sustainable and circular economy, where waste is viewed as a resource rather than a burden. By recovering energy from waste, we can decrease the extraction and consumption of non-renewable resources, thereby preserving these resources for future generations.
Challenges and Considerations
While energy recovery from waste offers numerous benefits, it is not without challenges.
1. Technical Challenges
- System Complexity: Depending on the source, capturing and converting energy efficiently can require complex systems with specific requirements for integration and maintenance.
- Matching Energy Supply and Demand: The recovered energy needs to be usable in a form that aligns with existing demand to avoid waste.
- Efficiency Limitations: No system is 100% efficient. There will always be some energy loss during the conversion process.
2. Financial Considerations
- Upfront Costs: Installing energy recovery systems can involve a significant initial investment, which may take time to recoup through energy savings.
- Maintenance Costs: These systems require ongoing maintenance to ensure optimal performance, adding to the overall operational expense.
3. Environmental Considerations
- Emissions Control: Some energy recovery processes, like waste-to-energy conversion, can generate emissions that need proper treatment to minimize environmental impact.
- Sustainability of Source: The source of the recovered energy needs to be sustainable. For example, recovering energy from burning non-renewable waste sources offers limited environmental benefit.
4. Social Considerations
- Public Perception: There can be public concern about the safety and environmental impact of certain energy recovery technologies, requiring clear communication and education.
- Equity and Access: Not everyone may have access to the benefits of energy recovery technologies due to cost or infrastructure limitations. Broader adoption strategies need to be considered.
Conclusion
Energy recovery is a valuable component of modern waste management strategies. By converting waste into usable forms of energy, it addresses the dual challenges of waste disposal and energy production. While not a replacement for traditional recycling, it complements recycling efforts and contributes to a more sustainable and resilient energy system. As technology evolves and public awareness grows, energy recovery will continue to play a pivotal role in the journey toward a cleaner and more sustainable future.














